Green Tea: A Journey Through History, Health Benefits, Brewing Techniques, and all FAQ’s answered
Green tea, with its delicate flavor and myriad health benefits, has been cherished for centuries in cultures around the world. From its origins in ancient China to its global popularity today, green tea continues to captivate tea enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals alike. In this blog, we will delve into the fascinating history of green tea, explore its numerous health benefits, and provide tips on how to brew the perfect cup.
- A Brief History of Green Tea
- Health Benefits of Green Tea
- Brewing the Perfect Cup of Green Tea
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions on Green Tea
- What is green tea, and how is it different from other types of tea?
- What are the health benefits of green tea?
- How is green tea processed?
- What are the different varieties of green tea?
- How should green tea be brewed for the best flavor?
- Can green tea help with weight loss?
- Are there any side effects of drinking green tea?
- What is the caffeine content of green tea compared to coffee?
- How does green tea affect metabolism?
- What is the role of antioxidants in green tea?
- How does green tea impact heart health?
- Can green tea help prevent cancer?
- Are there any benefits of green tea for skin health?
- What are some traditional uses of green tea in different cultures?
- How should green tea be stored to maintain its freshness?
- List of Darjeeling Tea Gardens
A Brief History of Green Tea
Green tea has a rich history that dates back over 4,000 years. According to legend, the discovery of tea is attributed to the Chinese Emperor Shen Nong in 2737 BC. One day, while boiling water in his garden, a few leaves from a nearby tea bush fell into his pot, creating a fragrant infusion. Intrigued by the aroma and flavor of the brew, the emperor tasted it and found it refreshing and invigorating. This serendipitous discovery marked the beginning of the tea-drinking tradition in China.
Over the centuries, green tea spread to other parts of Asia, including Japan, Korea, and Vietnam, where it became an integral part of their cultures. Each region developed its unique methods of cultivating and preparing green tea, resulting in a wide variety of flavors and styles.
Health Benefits of Green Tea
Green tea is renowned for its numerous health benefits, many of which are attributed to its high concentration of antioxidants and other beneficial compounds. Some of the key health benefits of green tea include:
- Rich in Antioxidants: Green tea is loaded with polyphenols, such as catechins and flavonoids, which help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, reducing the risk of chronic diseases like cancer and heart disease.
- Boosts Metabolism: The catechins in green tea have been shown to increase metabolism, helping to burn fat and improve weight loss.
- Improves Brain Function: Green tea contains caffeine and L-theanine, which can improve mood, alertness, and brain function.
- Supports Heart Health: Regular consumption of green tea is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, as it helps lower cholesterol and improve blood flow.
- May Reduce the Risk of Cancer: Some studies suggest that the antioxidants in green tea may help reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, although more research is needed in this area.

Brewing the Perfect Cup of Green Tea
To fully appreciate the flavor and health benefits of green tea, it’s essential to brew it correctly. Here’s a simple guide to brewing the perfect cup of green tea:
- Choose High-Quality Tea: Start with high-quality loose-leaf green tea for the best flavor.
- Water Temperature: Heat water to around 175°F (80°C). Water that is too hot can scald the tea leaves, resulting in a bitter brew.
- Steeping Time: Steep the tea for 2-3 minutes. Longer steeping times can extract more bitterness from the leaves.
- Enjoy Plain or with Honey: Green tea can be enjoyed plain or sweetened with a touch of honey for added flavor.
Conclusion
Green tea is not just a beverage; it’s a cultural phenomenon with a rich history and a plethora of health benefits. Whether you enjoy it for its delicate flavor or its numerous health benefits, green tea is sure to delight your senses and nourish your body. So, brew yourself a cup of green tea today and experience the magic of this ancient elixir.
Gelassen.in is your go-to source for all things tea-related. Stay tuned for more informative and engaging articles on tea, brewing techniques, and health benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions on Green Tea
Here are some questions related to green tea:
Green tea is a type of tea that is made from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant. What sets green tea apart from other types of tea, such as black tea and oolong tea, is the way it is processed.
What is green tea, and how is it different from other types of tea?
After the leaves are harvested, they undergo minimal oxidation, a process that causes the leaves to darken and change flavor. For green tea, oxidation is prevented by quickly steaming or pan-frying the leaves, which helps to preserve their natural green color and fresh flavor. This minimal processing helps to retain more of the tea’s natural antioxidants and nutrients, making green tea a popular choice for those seeking a healthful beverage.
What are the health benefits of green tea?
Green tea is renowned for its numerous health benefits, many of which are attributed to its high concentration of antioxidants and other beneficial compounds. Some of the key health benefits of green tea include:
- Rich in Antioxidants: Green tea is loaded with polyphenols, such as catechins and flavonoids, which help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, reducing the risk of chronic diseases like cancer and heart disease.
- Boosts Metabolism: The catechins in green tea have been shown to increase metabolism, helping to burn fat and improve weight loss.
- Improves Brain Function: Green tea contains caffeine and L-theanine, which can improve mood, alertness, and brain function.
- Supports Heart Health: Regular consumption of green tea is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, as it helps lower cholesterol and improve blood flow.
- May Reduce the Risk of Cancer: Some studies suggest that the antioxidants in green tea may help reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, although more research is needed in this area.
- Aids in Weight Loss: Green tea can help boost metabolism and increase fat burning, making it a popular choice for those looking to lose weight.
- Improves Dental Health: The catechins in green tea can help kill bacteria in the mouth, reducing the risk of cavities and improving overall dental health.
- May Lower the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: Some studies suggest that green tea may help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels, lowering the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Supports Longevity: Some studies have found that regular consumption of green tea is associated with a longer lifespan.
These are just a few of the many health benefits associated with green tea. Incorporating this beverage into your daily routine may help improve your overall health and well-being.
How is green tea processed?
Green tea is processed differently from other types of tea, such as black tea or oolong tea. The processing of green tea involves several key steps:
- Withering: After the tea leaves are harvested, they are spread out to wither, which helps reduce moisture content and make the leaves more pliable.
- Fixation: The withered leaves are then subjected to high heat, either through steaming or pan-firing. This heat treatment deactivates the enzymes responsible for oxidation, preserving the green color and fresh flavor of the leaves.
- Rolling: The leaves are rolled to break down their cell walls, releasing the natural juices and flavors.
- Drying: Finally, the leaves are dried to reduce their moisture content further and improve their shelf life.
The entire process is designed to minimize oxidation, which is why green tea retains its green color and fresh flavor. This minimal processing also helps preserve the tea’s natural antioxidants and nutrients, making it a popular choice for health-conscious individuals.
What are the different varieties of green tea?
There are several different varieties of green tea, each with its unique flavor profile and characteristics. Some of the most popular varieties include:
- Sencha: Sencha is one of the most popular types of green tea in Japan and is known for its grassy, slightly sweet flavor. It is made from whole tea leaves that are steamed, rolled, and dried.
- Matcha: Matcha is a powdered green tea that is made from finely ground tea leaves. It has a rich, umami flavor and is commonly used in traditional Japanese tea ceremonies.
- Dragonwell (Longjing): Dragonwell, or Longjing, is a famous Chinese green tea known for its flat, smooth leaves and sweet, nutty flavor. It is pan-fired to stop oxidation, giving it a distinctive roasted taste.
- Gunpowder: Gunpowder tea is a type of Chinese green tea that is rolled into small pellets, resembling gunpowder. It has a bold, smoky flavor and is often used in Moroccan mint tea.
- Gyokuro: Gyokuro is a high-quality Japanese green tea that is shaded for several weeks before harvest, which gives it a rich, sweet flavor and a deep green color.
- Hojicha: Hojicha is a roasted green tea from Japan that has a reddish-brown color and a toasty, caramel-like flavor. It is made by roasting sencha or bancha leaves at a high temperature.
These are just a few examples of the many varieties of green tea available. Each variety has its unique characteristics, making green tea a versatile and exciting beverage to explore.
How should green tea be brewed for the best flavor?
Brewing green tea is a delicate process that requires careful attention to detail to achieve the best flavor. Here’s a general guide for brewing green tea:
- Choose high-quality tea: Start with high-quality loose-leaf green tea for the best flavor.
- Use the right water: Use filtered water or spring water for the best results. Avoid using water that is too hard or has a strong taste, as it can affect the flavor of the tea.
- Heat the water: Heat water to around 175°F to 185°F (80°C to 85°C). Water that is too hot can scald the tea leaves, resulting in a bitter brew.
- Measure the tea: Use about 1 teaspoon of tea leaves per 8 ounces of water. Adjust the amount based on your taste preferences.
- Steeping time: Steep the tea for 2-3 minutes. Longer steeping times can extract more bitterness from the leaves.
- Strain and serve: Once the tea has steeped, strain out the leaves and pour the tea into cups. Green tea can be enjoyed plain or sweetened with a touch of honey for added flavor.
- Experiment with brewing methods: Some green teas, such as Japanese gyokuro, are best brewed at lower temperatures for a longer time, while others, like Chinese dragonwell, can handle higher temperatures. Experiment with different brewing methods to find the perfect balance for your taste.
By following these tips, you can brew a delicious cup of green tea that highlights its delicate flavor and natural sweetness.
Can green tea help with weight loss?
Yes, green tea can help with weight loss, although it is not a magic solution on its own. Green tea contains catechins, a type of antioxidant that has been shown to increase metabolism and promote fat burning. Additionally, green tea contains caffeine, which can also help boost metabolism and improve exercise performance, both of which can contribute to weight loss.
Some studies suggest that drinking green tea may help reduce body fat, particularly in the abdominal area. However, it’s important to note that while green tea can be a helpful addition to a healthy diet and exercise routine, it is not a substitute for a balanced lifestyle. To achieve and maintain weight loss, it’s essential to combine green tea consumption with a nutritious diet and regular physical activity.
Are there any side effects of drinking green tea?
While green tea is generally safe for most people when consumed in moderation, there are some potential side effects to be aware of:
- Caffeine Sensitivity: Green tea contains caffeine, which can cause side effects such as insomnia, nervousness, stomach upset, and rapid heartbeat in some individuals, especially when consumed in large amounts.
- Iron Absorption: Some studies suggest that the tannins in green tea can inhibit the absorption of iron from food. If you have iron deficiency or are at risk of iron deficiency, it may be best to consume green tea between meals rather than with meals.
- Stomach Irritation: Green tea can sometimes cause stomach irritation or upset, particularly in people who are sensitive to caffeine or have a history of stomach ulcers.
- Interactions with Medications: Green tea may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners, beta-blockers, and some antidepressants. If you are taking medication, it’s best to consult with your healthcare provider before adding green tea to your routine.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: While moderate consumption of green tea is generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, it’s best to consult with your healthcare provider to determine what’s right for you.
Overall, green tea is safe for most people when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. If you have any concerns or experience any negative side effects, it’s best to consult with your healthcare provider.
What is the caffeine content of green tea compared to coffee?
The caffeine content of green tea can vary depending on factors such as the type of tea, brewing time, and water temperature. On average, an 8-ounce cup of green tea contains about 20-45 milligrams of caffeine. In comparison, an 8-ounce cup of coffee typically contains 95 milligrams of caffeine.
This means that green tea generally contains less caffeine than coffee, making it a milder alternative for those looking to reduce their caffeine intake. However, the actual caffeine content can vary, so it’s essential to check the specific brand and type of green tea you are consuming if you are sensitive to caffeine.
How does green tea affect metabolism?
Green tea is believed to affect metabolism through its combination of caffeine and catechins, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which are potent antioxidants.
- Caffeine: Green tea contains caffeine, which is a stimulant that can increase energy expenditure (calories burned) and improve physical performance by mobilizing fatty acids from the fat tissues, making them available for use as energy.
- Catechins: EGCG and other catechins in green tea have been shown to boost metabolism by increasing the levels of hormones that tell fat cells to break down fat. They also inhibit the enzyme that breaks down norepinephrine, a hormone involved in the regulation of fat metabolism.
- Synergistic Effects: When combined, the caffeine and catechins in green tea have been shown to have synergistic effects on metabolism, leading to greater fat oxidation and overall energy expenditure.
While green tea can modestly boost metabolism and help with weight loss, it’s important to note that the effects are relatively small and may vary from person to person. Green tea is best used as part of a healthy diet and lifestyle for weight management.
What is the role of antioxidants in green tea?
Antioxidants play a crucial role in green tea and are one of the key reasons for its health benefits. Green tea is rich in polyphenols, particularly catechins, which are powerful antioxidants. Antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to aging and diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes.
The main antioxidants in green tea, such as epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), have been shown to have various health benefits, including:
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: The antioxidants in green tea help protect cells from damage and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes.
- Improved Brain Function: Some studies suggest that the antioxidants in green tea may help improve brain function and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Weight Loss: The catechins in green tea have been shown to increase metabolism and promote fat burning, making it a popular choice for those looking to lose weight.
- Improved Dental Health: The catechins in green tea can help kill bacteria in the mouth, reducing the risk of cavities and improving overall dental health.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Green tea antioxidants have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the body and protect against chronic diseases.
Overall, the antioxidants in green tea play a crucial role in promoting health and well-being. Incorporating green tea into your diet can be a delicious way to boost your antioxidant intake and support overall health.
How does green tea impact heart health?
Green tea has been studied for its potential impact on heart health, and several mechanisms have been proposed:
- Lowering Cholesterol: Some studies suggest that green tea may help lower LDL cholesterol levels (the “bad” cholesterol) while increasing HDL cholesterol levels (the “good” cholesterol), which can improve heart health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Reducing Blood Pressure: Green tea has been shown to have a modest lowering effect on blood pressure, which is beneficial for heart health. The antioxidants in green tea may help relax blood vessels and improve blood flow, which can help reduce the risk of hypertension and heart disease.
- Improving Arterial Function: Green tea has been found to improve the function of the endothelial cells lining the arteries, which can help regulate blood pressure and prevent the formation of blood clots.
- Reducing Inflammation: The antioxidants in green tea have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the body and protect against heart disease.
- Antioxidant Effects: The antioxidants in green tea can help protect the heart and blood vessels from damage caused by free radicals, which can contribute to heart disease.
Overall, while more research is needed, the current evidence suggests that green tea may have a positive impact on heart health when consumed as part of a healthy diet and lifestyle.
Can green tea help prevent cancer?
Green tea has been studied for its potential cancer-preventive effects, and while more research is needed, some studies suggest that green tea may help reduce the risk of certain types of cancer. Here’s how green tea may impact cancer prevention:
- Antioxidant Properties: Green tea is rich in antioxidants, particularly catechins, which have been shown to have protective effects against cancer by neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress, which can damage DNA and lead to cancer development.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: The antioxidants in green tea also have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce chronic inflammation, a key factor in the development of cancer.
- Cellular Effects: Some studies suggest that the catechins in green tea may interfere with the growth of cancer cells, inhibit the spread of tumors, and induce cancer cell death, although more research is needed to confirm these effects.
- Specific Cancers: While research is ongoing, some studies suggest that green tea may be particularly beneficial in reducing the risk of breast, prostate, colorectal, and lung cancers.
- Overall Diet and Lifestyle: It’s important to note that while green tea may offer some protective effects against cancer, it is just one part of a healthy diet and lifestyle. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption are also important for reducing cancer risk.
While green tea shows promise as a potential cancer preventive agent, more research is needed to fully understand its effects. It’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your diet or lifestyle, especially if you have a history of cancer or other health conditions.
Are there any benefits of green tea for skin health?
Green tea is believed to offer several benefits for skin health, thanks to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. Some potential benefits of green tea for skin health include:
- Anti-aging Effects: The antioxidants in green tea, particularly catechins, can help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, which can lead to premature aging of the skin. Green tea may help improve the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and sagging skin.
- Sun Protection: Some studies suggest that green tea polyphenols can help protect the skin from UV damage caused by sun exposure. While green tea cannot replace sunscreen, it may offer additional protection when used alongside sun protection measures.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Green tea has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce redness, irritation, and swelling associated with inflammatory skin conditions such as acne, rosacea, and eczema.
- Acne Treatment: The catechins in green tea have been shown to have antimicrobial properties that can help fight acne-causing bacteria. Green tea may also help reduce sebum production, which can contribute to acne.
- Skin Repair: Green tea may help promote skin repair and regeneration, thanks to its ability to stimulate the production of collagen, a protein that is essential for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness.
- Skin Brightening: Some studies suggest that green tea extract can help brighten the skin and improve overall complexion, thanks to its ability to inhibit melanin production and reduce hyperpigmentation.
Overall, while more research is needed to fully understand the effects of green tea on skin health, incorporating green tea into your skincare routine may offer several potential benefits for maintaining healthy, youthful-looking skin.
What are some traditional uses of green tea in different cultures?
Green tea has a long history of traditional uses in various cultures around the world. Some of the traditional uses of green tea include:
- China: In China, green tea has been used for thousands of years for its medicinal properties. It is often used to improve digestion, boost energy, and promote overall health and well-being. Green tea is also an integral part of Chinese tea culture and is often served during meals or as a gesture of hospitality.
- Japan: In Japan, green tea is deeply ingrained in the culture and is an essential part of daily life. Japanese green tea, such as matcha and sencha, is used in tea ceremonies, which are a traditional ritual that emphasizes mindfulness, respect, and tranquility. Green tea is also enjoyed as a refreshing beverage and is often served with sweets to balance its bitter flavor.
- Korea: In Korea, green tea is known as “nokcha” and is also an important part of the culture. It is often used to aid digestion, improve mental alertness, and promote relaxation. Green tea is also used in traditional Korean tea ceremonies, which are similar to those in Japan.
- India: In India, green tea is not as widely consumed as in other countries, but it is gaining popularity due to its health benefits. Green tea is often used in Ayurvedic medicine as a remedy for various ailments, including digestive issues, inflammation, and stress.
- Morocco: In Morocco, green tea is known as “Moroccan mint tea” and is a staple of the culture. It is made with green tea leaves, fresh mint leaves, and sugar, and is often served in small glasses as a gesture of hospitality.
These are just a few examples of the traditional uses of green tea in different cultures. Green tea has a long history of use as a beverage and medicinal remedy, and its popularity continues to grow around the world.
How should green tea be stored to maintain its freshness?
To maintain the freshness and flavor of green tea, it’s essential to store it properly. Here are some tips for storing green tea:
- Keep it airtight: Store green tea in an airtight container, such as a tin or a glass jar with a tight-fitting lid. This will help protect the tea from exposure to air, which can cause it to lose flavor and aroma.
- Keep it dry: Moisture can cause green tea to spoil and lose its flavor. Store green tea in a dry place away from sources of moisture, such as the kitchen sink or stove.
- Keep it cool: Heat can also cause green tea to lose its flavor. Store green tea in a cool place away from direct sunlight and heat sources, such as the stove or oven.
- Avoid odors: Green tea can absorb odors from other foods, so it’s best to store it away from strong-smelling foods, such as spices or onions.
- Use it promptly: Green tea is best when consumed fresh. Try to use it within a few months of purchase for the best flavor.
https://gelassen.in/product/giddapahar-green-tea-wonder-darjeeling-tea-garden/
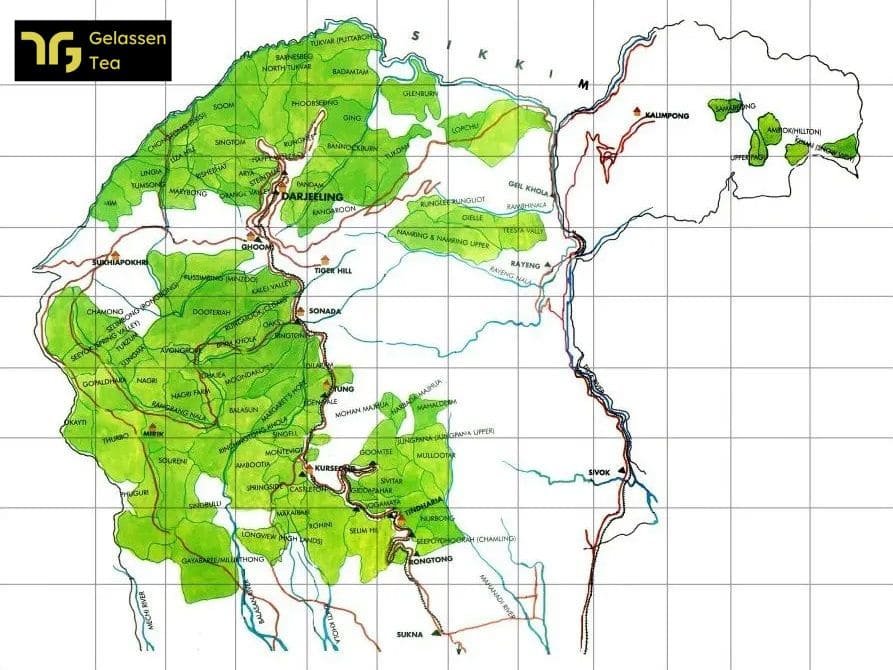
List of Darjeeling Tea Gardens
Explore the enchanting world of Darjeeling tea with our comprehensive list of Darjeeling tea gardens. Discover the rich history, stunning landscapes, and exquisite teas produced by these renowned estates. From the iconic Makaibari Tea Estate to the picturesque Steinthal Tea Estate, immerse yourself in the beauty and flavors of Darjeeling’s tea culture.






Leave a Reply